Introduction
Many people love cottage cheese. It is creamy, high in protein, and easy to eat. But some wonder, is cottage cheese inflammatory? The answer depends on your body and diet. Some dairy products can cause inflammation, while others may help reduce it.

Cottage cheese is a dairy product, like yogurt and eggs. Some dairy foods contain casein and lactose, which may lead to bloating or inflammation in some people. Others, however, are packed with probiotics, which can help with digestion.
Many people follow an anti-inflammatory diet to stay healthy. But is cottage cheese a good choice? Some say cottage cheese can fight inflammation, while others think it causes problems. In this article, we will explore both sides.
You will learn:
- How cottage cheese affects inflammation.
- What food make it healthy or harmful.
- How to eat it in a balanced way.
- The best ways to enjoy cottage cheese in meals.
If you love cottage cheese but worry about its effects, keep reading! You might be surprised by what you learn.
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Is Cottage Cheese Inflammatory? Effects, Benefits & Best Choices
- Can Cottage Cheese Cause Inflammation or Reduce It?
- How to Eat Cottage Cheese in an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
- Cottage Cheese and Inflammation: Myths vs. Facts
- Best Foods to Eat with Cottage Cheese
- Is Cottage Cheese Good or Bad for Inflammation?
- When Can Cottage Cheese Help Reduce Inflammation?
- FAQs: Cottage Cheese and Inflammation
- Conclusion: Should You Eat Cottage Cheese?
Is Cottage Cheese Inflammatory? Effects, Benefits & Best Choices
Cottage cheese is a popular dairy product, but many people wonder, is cottage cheese inflammatory? The answer is not simple. Some people digest it well, while others experience bloating or discomfort. It all depends on your body, diet, and the type of cottage cheese you eat.
This article explores how cottage cheese affects inflammation, whether it helps or harms your health, and the best ways to include it in your diet.
Can Cottage Cheese Cause Inflammation or Reduce It?
Dairy products affect people differently. Some experience inflammation after eating dairy, while others do not. Cottage cheese contains both casein and lactose, which can trigger inflammatory responses in some individuals. However, it also provides probiotics, which may reduce inflammation and support gut health.
How Dairy Affects Inflammation
Many people believe that dairy causes inflammation, but this is not always true. Some studies suggest that low-fat dairy products may actually help reduce inflammation, while full-fat dairy could have the opposite effect. Your body’s reaction depends on your tolerance to dairy and the type of cottage cheese you consume.
Casein and Lactose: Are They Problematic?
Cottage cheese contains two key components that may impact inflammation:
- Casein: A protein found in milk. Some people are sensitive to it, which can lead to digestive issues or inflammation.
- Lactose: A natural sugar in dairy. People with lactose intolerance may experience bloating, gas, or discomfort after consuming it.
If your body struggles with either of these, you may experience an inflammatory response after eating cottage cheese.

Does Cottage Cheese Have Anti-Inflammatory Benefits?
Not all dairy products increase inflammation. Some contain probiotics, which are beneficial bacteria that support digestion and gut health. Cottage cheese with live active cultures may help reduce inflammation and improve digestion.
If you are looking for an anti-inflammatory option, choose cottage cheese that contains probiotics. This type can support your gut and may reduce the risk of inflammation.
Full-Fat vs. Low-Fat Cottage Cheese: Which Is Better?
The fat content in cottage cheese may also play a role in inflammation:
- Full-fat cottage cheese: Contains saturated fats, which may contribute to inflammation in some cases.
- Low-fat or non-fat cottage cheese: Has less saturated fat and may be a better choice for reducing inflammation.
Choosing the right type depends on your dietary needs and how your body processes dairy. Therefore, if you are unsure, try different types of cottage cheese and monitor how you feel after eating them. Additionally, keeping a food diary can help you track any reactions and make more informed decisions about which variety suits you best

How to Eat Cottage Cheese in an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Cottage cheese can be part of a healthy, anti-inflammatory diet if you choose the right type and eat it with the right foods. While some varieties may cause inflammation, others help with digestion and overall health. To get the best results, you need to make smart choices and balance your meals.
Choose the Best Cottage Cheese for Inflammation
Not all cottage cheese is the same, so it is important to pick the right one. Some types contain ingredients that may cause inflammation, while others have nutrients that support a healthy body. To make the best choice, follow these tips:
- Look for probiotics because they help with digestion and may lower inflammation. Some brands add live and active cultures, which support gut health.
- Pick low-fat or non-fat options since they contain less saturated fat, which can reduce the risk of inflammation.
- Choose organic cottage cheese to avoid hormones and antibiotics, which some studies link to inflammation.
- Select low-sodium versions so you can prevent water retention and bloating, which may make inflammation worse.
Reading food labels carefully will help you find the healthiest option.

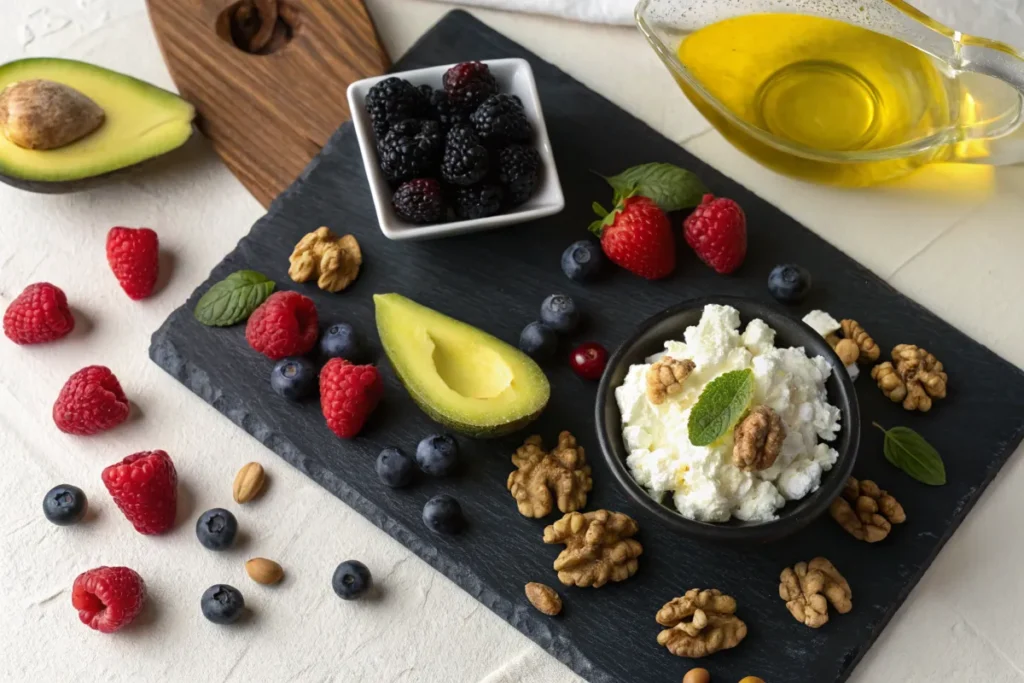
Pair Cottage Cheese with Anti-Inflammatory Foods
Eating cottage cheese with anti-inflammatory foods makes it even healthier. Some foods naturally fight inflammation while providing important vitamins and minerals. Try these tasty combinations:
- Cottage cheese with avocado because healthy fats in avocado help lower inflammation.
- Cottage cheese with berries since blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries contain antioxidants that protect the body.
- Cottage cheese with leafy greens like spinach, kale, and arugula, which provide vitamins that support digestion.
- Cottage cheese with nuts and seeds such as almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds, which supply fiber and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Cottage cheese with turmeric and honey because both ingredients have natural anti-inflammatory properties.
By adding these foods, you can turn cottage cheese into a nutrient-packed meal.
Avoid Ingredients That May Cause Inflammation
Some foods can increase inflammation, especially when combined with dairy. If you are sensitive to certain ingredients, try to limit these:
- Flavored cottage cheese since many brands add sugar and artificial ingredients, which may cause inflammation.
- Highly processed varieties because some contain preservatives and thickeners, which can upset digestion.
- Excess full-fat dairy since too much saturated fat may increase inflammation over time.
- Processed carbohydrates like white bread or sugary cereals, which raise blood sugar levels and may lead to inflammation.

Choosing whole, natural foods helps you enjoy the benefits of cottage cheese while avoiding unwanted effects.
How Often Should You Eat Cottage Cheese?
Cottage cheese can be a great addition to your diet, but moderation is important. To get the best results, follow these tips:
- Eat 1–2 servings per day so you can get enough protein and nutrients without too much dairy.
- Pair it with anti-inflammatory foods to make it even healthier. Adding fresh fruits, vegetables, or healthy fats improves its benefits.
- Listen to your body and pay attention to how you feel after eating it. If you experience bloating or discomfort, try a probiotic-rich version or eat smaller portions.
By making smart choices, you can enjoy cottage cheese without worrying about inflammation.
Cottage Cheese and Inflammation: Myths vs. Facts
Many people ask, is cottage cheese inflammatory? Some believe that all dairy causes inflammation, while others think certain types may actually help reduce it. The truth is that cottage cheese affects people differently. While some digest it easily, others experience bloating or discomfort. Understanding the facts helps you decide if it fits into your diet.
Does Cottage Cheese Always Cause Inflammation?
Cottage cheese, like other dairy products, can have different effects on inflammation. Some people tolerate it well, while others may have digestive issues. The two main components that influence this are casein and lactose.
Casein and Lactose: Do They Cause Problems?
- Casein is a protein in dairy that may cause an immune response in some individuals. This reaction can lead to mild inflammation in sensitive people. However, most people digest it without any issues.
- Lactose is a natural sugar in milk that some people cannot break down. When this happens, it may cause bloating and discomfort. In some cases, this irritation can lead to inflammation.
If you have digestive issues after eating cottage cheese, these components might be the cause. Switching to a lactose-free or probiotic-rich version could help.

Full-Fat vs. Low-Fat Cottage Cheese: Which Is Better?
The type of cottage cheese you eat also matters. Research suggests that:
- Full-fat cottage cheese contains more saturated fat, which may contribute to inflammation if eaten in large amounts.
- Low-fat and non-fat versions have less saturated fat, making them a better option for those who want to lower inflammation risks.
Choosing low-fat cottage cheese and eating it with anti-inflammatory foods can help balance its effects.
Can Cottage Cheese Help Reduce Inflammation?
Although some worry about dairy and inflammation, research shows that certain types of cottage cheese may actually support gut health and reduce inflammation.
Probiotics and Their Benefits
Some brands of cottage cheese contain probiotics, which are beneficial bacteria that improve digestion. Probiotics help maintain gut balance, and a healthy gut can lower inflammation levels.
To get these benefits, choose cottage cheese labeled “live and active cultures.” This type contains probiotics that support digestion and may reduce bloating and discomfort.
Nutrients in Cottage Cheese That Support Health
Cottage cheese is packed with protein, calcium, and B vitamins, which all play a role in overall health. These nutrients help:
- Support muscle recovery after exercise.
- Keep bones strong and reduce the risk of bone loss.
- Improve energy levels and support metabolism.
Eating cottage cheese along with other healthy foods can help the body manage inflammation naturally.
Best Foods to Eat with Cottage Cheese
Pairing cottage cheese with the right foods makes it even healthier. Try these combinations to help reduce inflammation:
- Cottage cheese with avocado because healthy fats in avocado may lower inflammation.
- Cottage cheese with berries since blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are rich in antioxidants.
- Cottage cheese with leafy greens like spinach and kale, which contain vitamins that support digestion.
- Cottage cheese with nuts and seeds such as almonds, walnuts, and flaxseeds, which provide omega-3 fatty acids that support heart health.
By choosing the right foods, you can enjoy cottage cheese without worrying about inflammation.
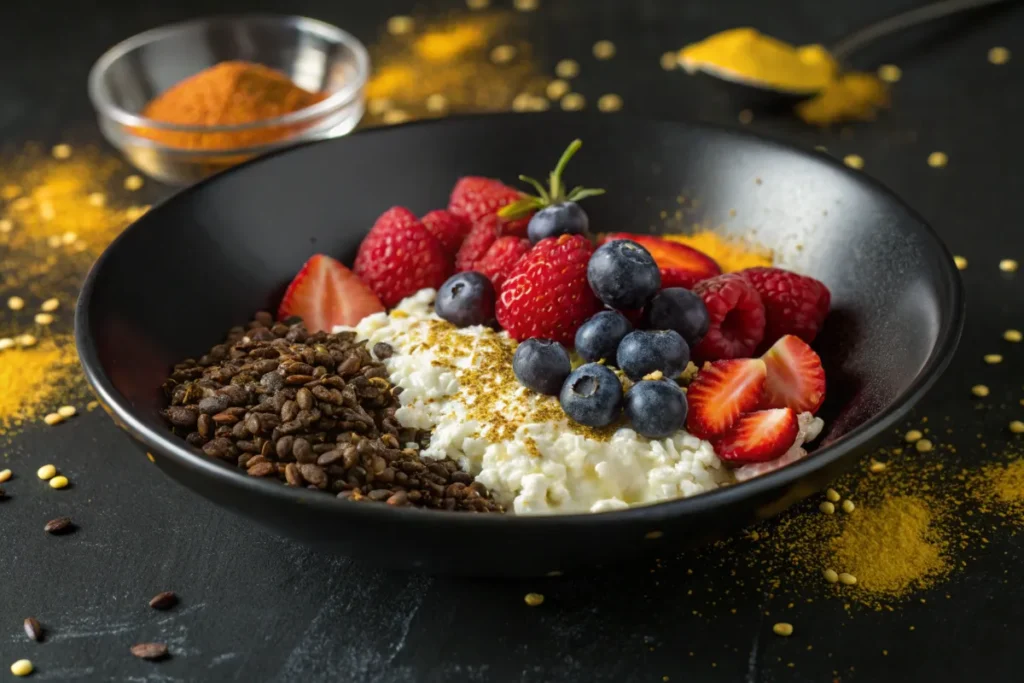

Is Cottage Cheese Good or Bad for Inflammation?
Cottage cheese is a popular dairy food, but many people wonder, is cottage cheese inflammatory? Some say it causes inflammation, while others believe it has health benefits. Understanding how it affects the body can help you decide if it belongs in your diet.
When Can Cottage Cheese Cause Inflammation?
Cottage cheese is nutritious, but certain factors may lead to inflammation in some people. Knowing what to watch for can help you avoid discomfort.
Lactose Intolerance and Digestion Issues
Many dairy products contain lactose, a natural sugar that some people cannot digest. When lactose is not broken down properly, it can cause:
- Bloating and gas, which may lead to inflammation in the gut.
- Stomach pain and discomfort after eating dairy.
- Diarrhea or digestive upset in people who are lactose intolerant.
If you have trouble with dairy, choosing lactose-free cottage cheese can help prevent these issues.
Saturated Fat and Inflammation
Cottage cheese, especially the full-fat variety, contains saturated fat, which may contribute to inflammation if eaten in large amounts. Studies suggest that too much saturated fat can:
- Raise cholesterol levels, which may lead to heart problems.
- Trigger inflammation, especially in people with existing health conditions.
- Cause weight gain, which can put stress on the body.
To reduce these risks, it is best to choose low-fat or non-fat cottage cheese as part of a good diet.
When Can Cottage Cheese Help Reduce Inflammation?
Not all dairy products increase inflammation. In fact, certain types of cottage cheese may help fight it.
Probiotics and Gut Health
Some brands add probiotics, which are good bacteria that help digestion. These live cultures can:
- Improve gut health by balancing bacteria in the intestines.
- Reduce bloating and ease stomach discomfort.
- Strengthen the immune system, which helps fight inflammation.
To get these benefits, look for cottage cheese labeled “live and active cultures.”
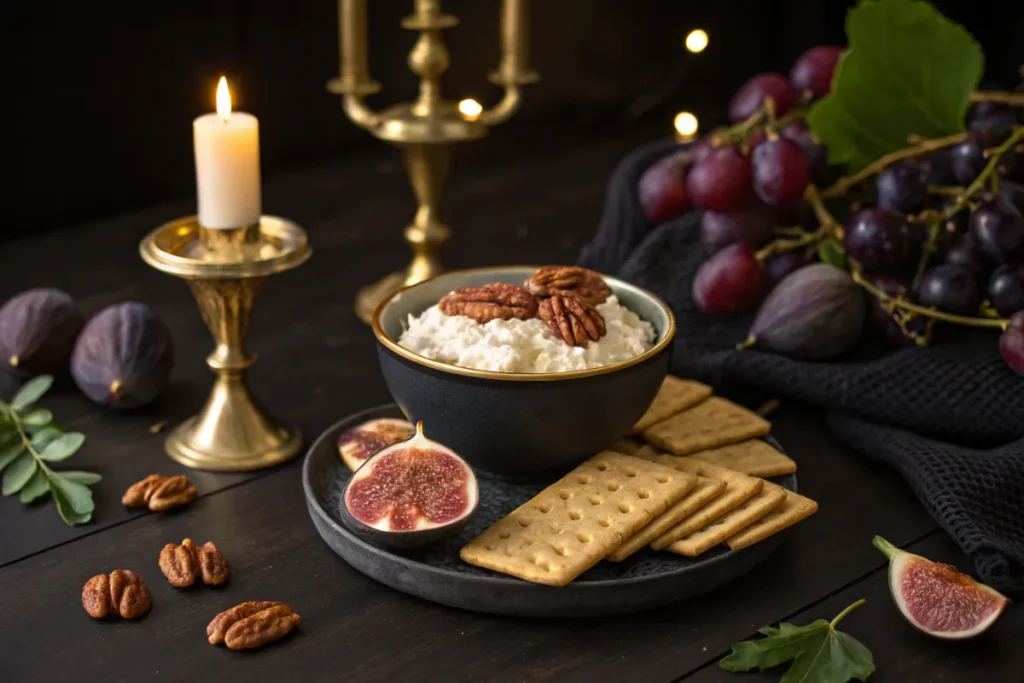

Essential Nutrients That Support the Body
Cottage cheese is packed with protein, calcium, and vitamins, which are important for overall health. These nutrients help:
- Support muscles by providing high-quality protein.
- Keep bones strong with calcium and vitamin D.
- Boost energy levels by supplying B vitamins.
When eaten in moderation and paired with anti-inflammatory foods, cottage cheese can be part of a healthy diet.
FAQs: Cottage Cheese and Inflammation
Cottage cheese may cause inflammation in some people, especially those who have trouble digesting lactose or casein. These dairy components can lead to bloating, gas, or stomach pain. However, some types of cottage cheese contain probiotics, which may help with digestion and reduce inflammation. Choosing low-fat or lactose-free versions can also make it easier to digest.
Although cottage cheese is healthy, it has some downsides. Here are a few things to watch for:
Lactose intolerance – Some people cannot digest lactose, which may lead to stomach problems.
High salt content – Many brands contain a lot of salt, which may increase blood pressure.
Saturated fat – Full-fat cottage cheese has more fat, which may lead to weight gain if eaten too often.
To avoid these problems, try low-fat, low-sodium, or lactose-free cottage cheese instead.
Some dairy products may increase inflammation more than others. The most common ones include:
Whole milk – Contains more fat, which may cause inflammation in some people.
Processed cheese – Often has artificial ingredients that may upset digestion.
Flavored yogurt – Contains added sugar, which may lead to weight gain and other health issues.
To lower inflammation, it is best to choose plain, low-fat, and unsweetened dairy products.
Some cheeses may help fight inflammation because they are easier to digest and contain healthy nutrients. The best choices include:
Probiotic cottage cheese – Contains live bacteria that support digestion.
Goat cheese – Has less lactose, making it easier on the stomach.
Feta cheese – Made from sheep’s milk, which some people digest better.
Aged cheeses (like Parmesan) – Have lower lactose levels, reducing the chance of stomach issues.
Eating these cheeses instead of processed ones may help reduce inflammation.
Conclusion: Should You Eat Cottage Cheese?
Cottage cheese can be a healthy choice, but it depends on how your body reacts to dairy. Some people digest it easily, while others may experience bloating or discomfort. The good news is that low-fat, lactose-free, and probiotic-rich options make it easier to enjoy without issues.
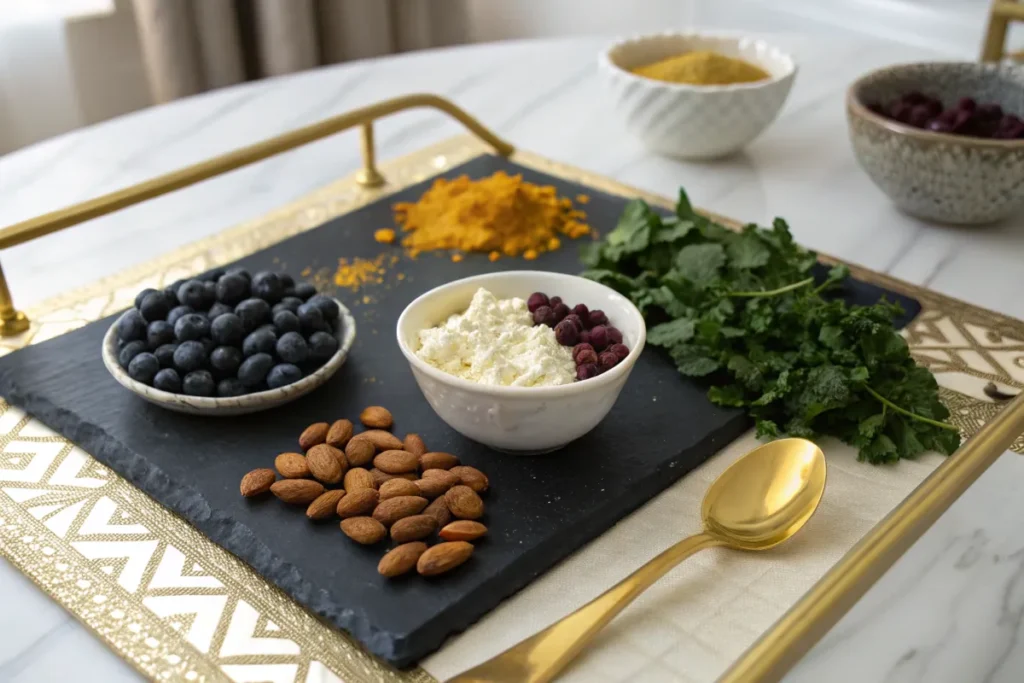

If you want to reduce inflammation, pairing cottage cheese with anti-inflammatory foods like berries, nuts, and leafy greens can help. Also, choosing low-sodium and organic versions can make a difference.
In the end, cottage cheese can be a great source of protein, calcium, and vitamins when eaten in moderation. If you pay attention to your body and make smart choices, you can enjoy its benefits without worrying about inflammation.

